Patanjali, Dabur Among Top Brands Adulterating Honey with Chinese Syrups: CSE

Representational image. | Image Courtesy: pixabay
With the ongoing pandemic, a significant section of Indians have turned to popular and trusted immunity boosters to keep themselves safe. With this, the market for honey has been booming, however, bee keepers are suffering an enormous price crash.
An investigation by the Centre of Science and Environment, released in Delhi on December 2, has revealed nefarious adulteration in honey designed to bypass purity tests in India and massive implications for the health of Indians.
The four-month long investigation conducted across laboratory studies in India and Germany reveal rampant adulteration in honey sold by major brands in India – 77% of samples were found adulterated with sugar syrup. Only three out of 13 brands pass the internationally accepted Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) test as Indian standards for honey purity cannot detect the adulteration.
CSE food researchers selected 13 top and smaller brands of processed and raw honey being sold in India. “Samples of these brands were first tested at the Centre for Analysis and Learning in Livestock and Food (CALF) at National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) in Gujarat. Almost all the top brands (except Apis Himalaya) passed the tests of purity, while a few smaller brands failed the tests to detect C4 sugar – call it basic adulteration using cane sugar. But when the same brands were tested using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) – laboratory tests currently being used globally to check for such modified sugar syrups – almost all big and small brands failed. Out of the 13 brands tests, only three passed the NMR test, which was done by a specialised laboratory in Germany,” the report states.
Also read: Can Big Ads and Tall Claims Guarantee Purity of Honey? No, Reveals Test
“What we found was shocking,” said Amit Khurana, programme director of CSE’s Food Safety and Toxins team. “It shows how the business of adulteration has evolved so that it can pass the stipulated tests in India. Our concern is not just that the honey we eat is adulterated, but that this adulteration is difficult to catch. In fact, we have found that the sugar syrups are designed so that they can go undetected,” he added.
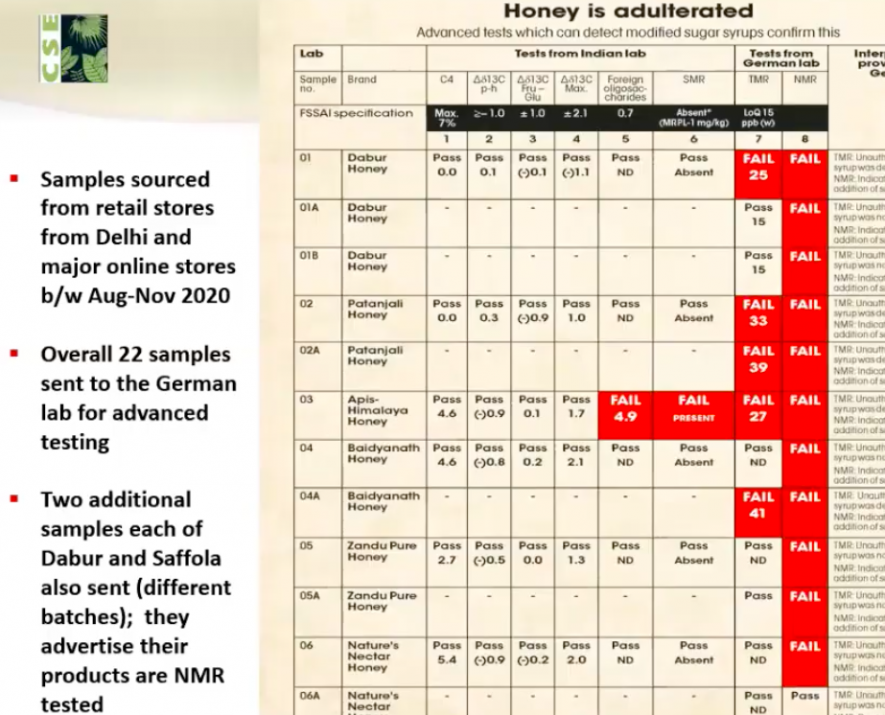
Out of 22 samples tested, only five passed all the tests. Honey samples from leading brands such as Dabur, Patanjali, Baidyanath, Zandu, Hitkari and Apis Himalaya, all failed the NMR test.
Only 3 out of the 13 brands – Saffola, Markfed Sohna and Nature’s Nectar (one out of two samples) -- passed all the tests.
As of August 1, 2020, NMR tests have been made mandatory in India for honey that is meant for export, suggesting that the Indian government is aware of this adulteration business and the need for more advanced tests.
Speaking at the launch, Sunita Narain, the executive director of CSE said, “Honey is a natural substance and is being consumed extensively because of its immunity boosting potential, but it is also the most adulterated substance. Through our investigation we have been able to reveal how sugar syrups--called the fructose syrups were being sold across popular Chinese websites like Alibaba, claiming to pass Indian safety standards.”
The leads on the investigation started when beekeepers across UP, Uttarakhand and several other states claimed that the Chinese had set up manufacturing of this sugar syrup in India which could bypass the tests.
The investigation also revealed serious lapses on the part of the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) and the Indian government, which has been changing its testing standards regularly.
Previously in 2017, the government amended the testing standards to include C3 and C4 types of sugar which are modified sugars which could adulterate the honey. This standard, notified in 2018, however, was removed by 2019.
CSE revealed that the economics of adulteration remained the real exposé. While adulterated honey was being sold at Rs. 60-68 per kilogram, natural-unadulterated honey was costing approximately Rs. 120. Further, “luring the businesses to flout norms was the effort of staying in touch with individual beekeepers and related businesses” it said.
Get the latest reports & analysis with people's perspective on Protests, movements & deep analytical videos, discussions of the current affairs in your Telegram app. Subscribe to NewsClick's Telegram channel & get Real-Time updates on stories, as they get published on our website.