Alarming Levels of Deadly Chemical in India’s Rivers, Says Study

A recent study “Dirty Trail: Detergent to Water Bodies” by Toxics Link, an environmental NGO, has found alarming levels of toxic chemical nonylphenol in detergents and river water across India. Water samples from various rivers which flow through different geographical locations- Garh Ganga and Hindon in Uttar Pradesh, Krishna in Adhra Pradesh, Tapti in Gujarat, Bandi in Rajasthan, Mahanadi in Odisha and Ambazari lake in Nagpur and detergent samples from the local markets in Delhi were analysed in the study.
As per the study, nonylphenol is “a xenobiotic and an endocrine disrupting chemical [which] is used largely in the production of nonylphenol ethoxylates (NPE) that is extensively used as a surfactant and in other industrial applications as well as in day to day consumer products.”
These NPEs “generally break down to nonylphenol in natural environmental conditions and enters into the ecosystem” and enters into “the food chain where it bio-accumulates and can pose serious environmental and health risks.” The study also points out that USA, European Union and China have acknowledged the menace of this chemical and there are restrictions on its use in various processes by shifting to safer alternatives.
However, while the aforementioned countries have prohibited the use of nonylphenon from detergents long ago, India has prohibited its use only in cosmetic products. But, the study says, there is “no regulation on its use in surfactants or other consumer products and there is no public information available on the possible impacts of the chemical and to minimise the risks associated with it.”
In India, there are no specific standards for Nonylphenol or Nonylphenol ethoxylates for water and waste water; however, standards for Phenolic compounds are listed in the standards for drinking water. The Bureau of Indian Standards [IS 4707 (Part 2:2009)] has prohibited the use of Nonylphenol in cosmetics.
In the study, the water samples were collected from two different points– point one and point two- of the river to get an understanding on the impact of anthropogenic activities on Nonylphenol concentration. The point before the anthropogenic activity (industrial discharge and washing of clothes) was considered as the point one and the point after anthropogenic activity was considered as point two. The study clearly shows that there is a correlation between high concentration of Nonlyphenol and anthropogenic activities since the concentration of Nonylphenol was much higher at point two.
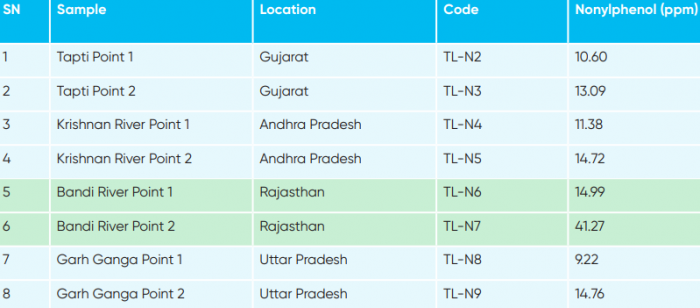
Concentration of Nonylphenol in point 1 and point 2 in different rivers
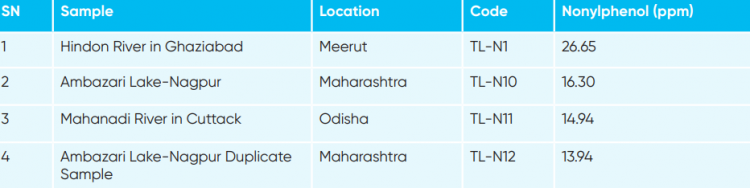
Concentration of Nonylphenol in other surface water samples
In the case of detergents, all of the 12 analysed samples detected Nonylphenol with concentration varied between 0.82 and 11.92 weight per cent (wt%).
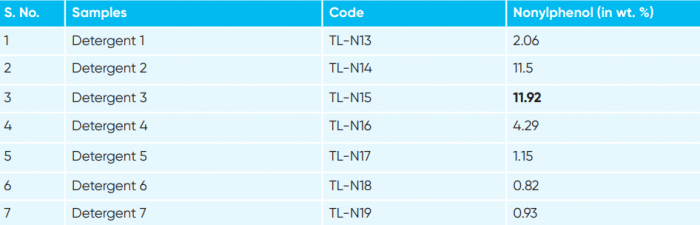
Concentration of Nonylphenol in detergent samples
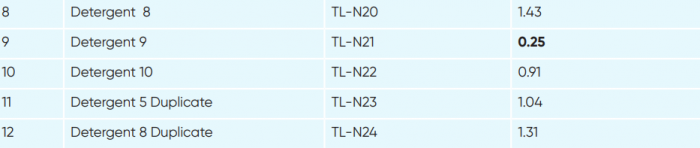
Concentration of Nonylphenol in detergent samples
It is important to note that the highest concentration of Nonylphenol was detected in the river Bandi in Rajasthan which is a hub of textile and other industries. Its quantity is also high in the river samples including Ganga.
Also, concentration in the detergent samples is found to be very high in the products of international corporations whereas they have declared their products to be free of Nonylphenol in other countries.
Impacts of Nonylphenol on Human Health
Various empirical studies depict human health impacts of Nonylphenol that is a persistent, toxic and bioaccumulative chemical which acts as a hormone disruptor and can be responsible for a number of adverse effects on human health.
If Nonylphenol enters the human body, it is rapidly and extensively absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract from where it is widely distributed throughout the body. Humans are getting exposed to NP through water, soil, food crops, paints, cosmetics, etc, while the largest contributor to the exposure is intake of fish.
Get the latest reports & analysis with people's perspective on Protests, movements & deep analytical videos, discussions of the current affairs in your Telegram app. Subscribe to NewsClick's Telegram channel & get Real-Time updates on stories, as they get published on our website.















