How Serious Is the Threat of Coronavirus

COVID-19 is yet to be declared a pandemic by World Health Organisation (WHO), but the rate of its spread is undoubtedly alarming. According to the reports of WHO, till March 2, the total number of countries outside China that have registered confirmed cases of infection are 65. The majorly affected countries are South Korea, Italy and Iran—Korea has 4,212 total confirmed cases with 476 new cases and 22 total deaths; Italy has 1,689 confirmed cases with 561 new cases and 35 deaths, while Iran has 978 confirmed cases with 385 new cases and a total death toll of 54.
The rise in cases outside China from December 2019 till March 2 are given in the graph below, which is produced by WHO.
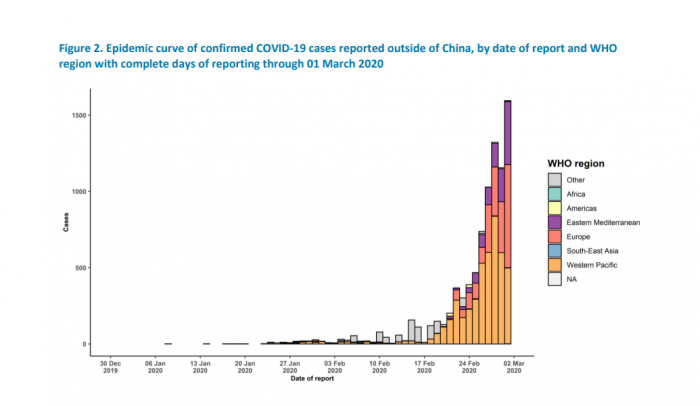
Graph Source: WHO.int
While new countries are getting affected, in China, the epicentre of the epidemic, the number of new infections have already started to wane. The country reported its lowest number of new cases in more than a month on Tuesday, with 125 confirmed infection and 31 deaths till March 2. In US, six new deaths have been reported due to the infection.
The epidemic curve of the last 12 days comparing China and outside is given below:
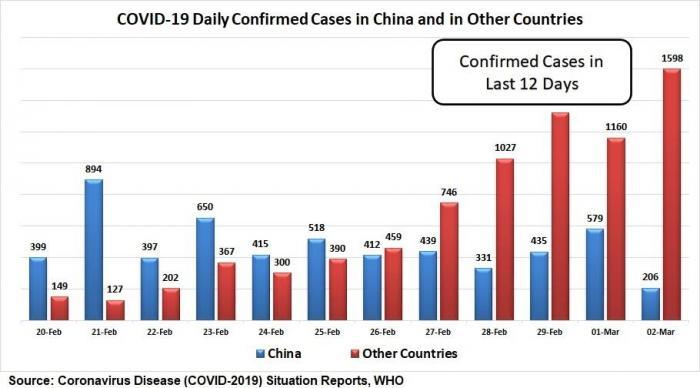
With the possibility of COVID-19 becoming a pandemic now, what every country needs to do is better planning for precaution and early preventions. In this regard, the model of handling the panic of the epidemic produced by China, can be taken into consideration. The WHO-China Joint Mission on COVID-19 also applauded China’s aggressive style in handling the epidemic. The scientifically driven approach adopted by China included case finding and contract tracing along with huge-scaled quarantine. It should be mentioned here that the entire Hubei Province, which was at the centre of the outbreak was locked down, where millions of its citizens were stuck, but with the availability of all facilities needed for day to day life and the extra medical facilities needed.
R0 or the Basic Reproduction Number:
The R0, pronounced as R naught or the basic reproduction number is a quantitative term to assess how infectious a disease is. R naught signifies the average of how many people an already infected person can pass on the infection to. If the R0 is less than one, the outbreak dies and when it exceeds one, the infection spreads. Highly infectious virus such as measles or bacteria such as tuberculosis have a high value of R0. The R0 for measles is between 10 and 20 and for tuberculosis it is 10. The outbreak which occurred in 2013 due to another kind of coronavirus, SARS, had an R0 value of around 3.
The novel coronavirus causing COVID-19 is reported to have an R0 value of around 4.08. This was calculated by Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Automation and University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. This figure is higher than the estimation of WHO, which says it is 1.4 to 2.5.
With a considerably higher R0 value, and in the absence of a vaccine, the best way of stopping further spread of the infection is to prepare in advance to trace people and keeping them in isolation for the period till the infection ceases. Alongside, hospital facilities including respiratory support system such as ventilators and up to date ICU have to be kept ready.
Also read: Coronavirus: 6 Cases 'High-Viral Load' Detected in Agra
Get the latest reports & analysis with people's perspective on Protests, movements & deep analytical videos, discussions of the current affairs in your Telegram app. Subscribe to NewsClick's Telegram channel & get Real-Time updates on stories, as they get published on our website.