Astronauts Conduct First Spacewalk on China's Space Station
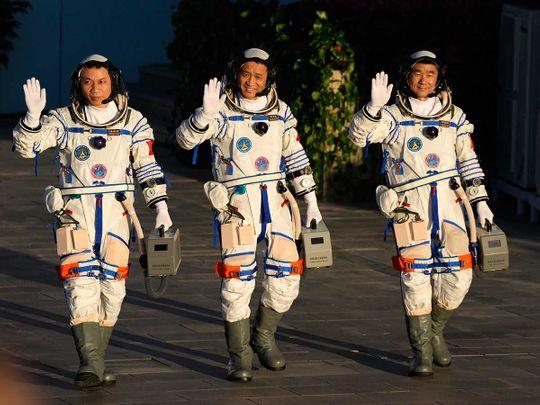

Chinese astronauts, from left, Tang Hongbo, Nie Haisheng, and Liu Boming. Image Courtesy: AP
In April this year, China successfully placed the Tiangong space station into orbit and now, for the first time, two astronauts walked outside the space station for nearly seven hours. Liu Boming and Tang Hongbo started the spacewalk on July 4th at round 8.00 am (Beijing Time). Liu was first to exit the core module of the space station, named Tianhe (it means harmony of the heavens in English) followed by Tang, around three hours later.
In June, three astronauts aboard the Shenzhou-12 spacecraft were blasted off to the space station which they reached after a journey of over seven hours.
While two of the three astronauts exited the space station for conducting extra-vehicular activities, the other was inside and helped them to carry out their spacewalk. The two astronauts’ tasks outside the space station included elevating a panoramic camera outside Tianhe, the core module of space station, and testing the robotic arm of the station. The robotic arms will be used in the future to transfer other modules of the space station. The astronauts reportedly installed foot stops on the robotic arm and carried out the rest of the assembly work with its help. The astronauts are supposed to be in the space station for three months, which will be the longest-crewed mission by China.
Notably, this was the first time that Chinese astronauts went outside a spacecraft after 2008, when Zhai Zhiagang conducted such a spacewalk and China became the third country to have completed the feat after the erstwhile Soviet Union and the US. This is also the first crewed mission in the past five years.
The Chinese space agency plans for a total of 11 launches in total till the end of next year which will include three more crewed missions. The space agency will also deliver two more lab modules to be docked to the space station, thus expanding it.
The Tiangong Space Station
Tiangong is the successor to Tiangong-1 and Tiangong-2, the Chinese space laboratories launched in 2011 and 2016 respectively. The Chinese space station is designed on similar lines of the ISS (International Space Station) operated by US, Russia, Japan, Canada and the European Space Agency.
Tiangong primarily consists of three components — a core module and two laboratories. The core module or capsule, the Tianhe is the size of a bus. It contains the life support system along with the control system. Weighing about 20 tons, the Tianhe capsule is the heaviest spacecraft ever made by China.
The Tianhe capsule is already in orbit and by 2022, the other two components of the Tiangong space station are expected to be clubbed with it. With that, the space station will expand to its full capacity of carrying out experiments of scientific and technological importance. The space station will ultimately have 14 internal experiment racks and 50 external ports. Combined, these will make the space station capable of conducting space studies.
Tianhe, the core module, has one-fifth the mass of the ISS and can accommodate three astronauts at a time. This core module was launched on April 29 from the Hianan Island in China courtesy the Long March 5B rocket.
The rockets used by Chinese Space Agency have one core stage accompanied by four boosters. The Long March 5B has a weight of about 940 tons with a full fuel tank and can take 28 tons into the space. These kinds of rockets will be used by China delivering modules and astronauts to the space station.
The Chinese space station – after its expansion is complete in 2022 – is expected to have a lifetime of ten years. On the other hand, the ISS lifetime will most likely expire by 2028 or sooner.
After the successful launch of the crewed Shenzhou-12 spacecraft, Chinese authorities have expressed interest in international cooperation for the future for a more collaborative scientific exploration of space.
Get the latest reports & analysis with people's perspective on Protests, movements & deep analytical videos, discussions of the current affairs in your Telegram app. Subscribe to NewsClick's Telegram channel & get Real-Time updates on stories, as they get published on our website.