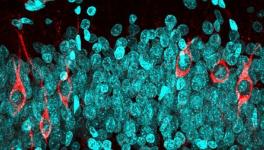
Brain Cells’ Ability to Revamp Genetic Architecture Could be Link to Alzheimer’s: New Study
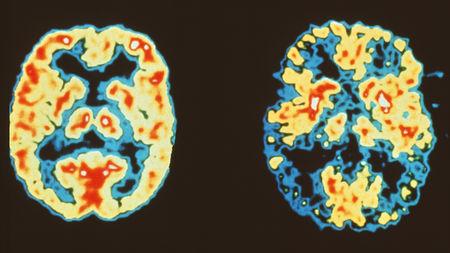
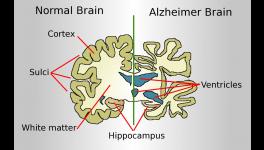
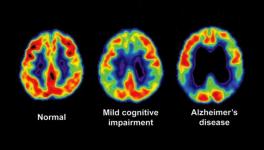
Brains without (left) and with (right) Alzheimer’s disease; Figure courtesy Science Magazine
The diversity of human brain function may not be encoded within a constant genetic blueprint; neurons can reshuffle their genes, a new study published in Nature reveals. This modification of the neurons’ genetic architecture may increase the protein variety in the brain, but it may also be related to Alzheimer’s disease, the study suggests.
The researchers analysed neurons from six healthy elderly people and seven patients reported to have Alzheimer’s disease. The patients had the most common form of Alzheimer’s - the non-inherited one. The researchers tested whether the brain cells got different forms of the gene for amyloid precursor protein (APP). Amyloid is the protein that forms plaques in the brain cells of people suffering from Alzheimer’s disease. The researchers considered APP as a good candidate because in a previous study they found that the gene for APP can have extra copies in the cells of Alzheimer’s patients. The increase arises from the process of somatic gene recombination.
What is more interesting, the Nature paper reports that the APP gene doesn’t make one or two extra copies, in fact, it produces thousands of different versions of the gene. In some of the versions, single nucleotide bases, the building blocks of the genetic code, are switched while in other versions they found that a portion of the DNA is removed and the remaining portions knitted together. They confirmed that neurons of Alzheimer’s patients contain six times more varieties of the APP protein than healthy people.
Also Read: Alzheimer’s May Spread Through the Brain Like an Infection
Somatic gene recombination, the process through which the inherited gene sequences are changed in the lifetime, is the way the neurons change their genetic architecture. Somatic recombination has been observed in some types of cells earlier and also in carcinogenesis—cancer formation, but existence of this recombination process in brain cells has been reported for the first time in this study.
Also Read: Regular, Good Quality Sleep Could Be a Way to Prevent Alzheimer’s
WHICH CELLS UNDERGO SOMATIC GENE RECOMBINATION
The reshuffling of genes by certain types of cells was discovered way back in 1970. The immune cells are the ones that till now have been established as the cells capable of undergoing somatic recombination. The T cell and B cell receptor genes are subjected to recombination through a mechanism called V (D) J recombination. The B cell can give rise to some 1 quadrillion types of antibodies to fight the enormous range of bacteria, virus and other types of pathogens. The somatic recombination confers these immune cells with the ability to produce a large variety of defence products.
WHAT CAUSES GENETIC RESHUFFLING IN NEURONS:
According to the researchers, one enzyme called the Reverse Transcriptase (RT) is the crucial factor in giving rise to the neurons’ genetic reshuffling. RT is a specific type of enzyme that produces DNA copies from RNA molecules. In the normal cellular process, when a neuron makes an RNA copy, the RT can make a DNA copy out of it which in turn slips back into the genome. In doing so, RT can make a different copy of the DNA from the original one. This makes a different copy of the APP protein.
Some scientists raise the concern of the necessity of more evidences in support of the Reverse Transcriptase hypothesis. Virologist John Coffin of Tufts University in Boston comments in Science, “Although it looks like that RT is involved, there’s a lot of work to do to establish that it is.”
The findings are yet to be reproduced in other labs. Nevertheless, if these unusual and unexpected findings get confirmed, then genetic reshuffling of neurons could also be found involved in other neurological diseases like Parkinson’s disease.
Get the latest reports & analysis with people's perspective on Protests, movements & deep analytical videos, discussions of the current affairs in your Telegram app. Subscribe to NewsClick's Telegram channel & get Real-Time updates on stories, as they get published on our website.